CIPS Global Commercial Strategy L6M2 Exam Dumps: Updated Questions & Answers (February 2026)
Compare and contrast an aggressive and conservative approach to business funding.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Comparison of Aggressive vs. Conservative Business Funding Approaches
Introduction
Businesses adopt differentfunding strategiesbased on theirrisk tolerance, growth objectives, and financial stability. Two contrasting approaches to business funding are:
Aggressive Funding Approach– Focuses onhigh-risk, high-reward strategieswithmore debt and short-term financingto fuel rapid expansion.
Conservative Funding Approach– Emphasizesfinancial stability, risk aversion, and long-term security, often relying onequity and retained earningsto fund operations.
Each approach has advantages and risks, influencing a company’sliquidity, cost of capital, and financial sustainability.
1. Aggressive Business Funding Approach????(High Risk, High Reward)
Definition
Anaggressive funding strategyinvolves maximizingshort-term debt, high leverage, and minimal cash reservestoaccelerate growth and expansion.
✅Key Characteristics:
Relies heavily on debt financing(bank loans, corporate bonds, short-term credit).
Prioritizes rapid growth and high returnsover financial security.
Uses minimal equity financingto avoid ownership dilution.
Maintains low cash reserves, assuming cash flows will cover liabilities.
????Example:
Startups and tech firms (e.g., Tesla, Uber, Amazon in early years)oftenborrow aggressivelyto scale rapidly.
Private equity firmsfund acquisitions using high leverage to maximize returns.
Advantages of Aggressive Funding
✔Faster business expansion– Capital is readily available for investments.✔Higher return potential– More funds are allocated to revenue-generating activities.✔Lower equity dilution– Existing shareholders maintain control as funding is primarily debt-based.
Disadvantages of Aggressive Funding
❌High financial risk– Heavy debt increases vulnerability to economic downturns.❌Liquidity problems– Low cash reserves can cause issues during slow revenue periods.❌Higher borrowing costs– Lenders charge higher interest due to the risk involved.
????Best for:Fast-growing companies, high-risk industries, and businesses with predictable cash flows.
2. Conservative Business Funding Approach????(Low Risk, Long-Term Stability)
Definition
Aconservative funding strategyfocuses onlow debt levels, high liquidity, and long-term financingto ensurefinancial stability and steady growth.
✅Key Characteristics:
Uses retained earnings and equity financingover debt.
Minimizes reliance on short-term creditto avoid financial pressure.
Maintains high cash reservesfor financial security.
Focuses on steady, sustainable growthrather than rapid expansion.
????Example:
Berkshire Hathaway (Warren Buffett’s company)follows aconservative funding model, relying on retained earnings rather than excessive debt.
Family-owned businessesoften prioritize financial stability over rapid expansion.
Advantages of Conservative Funding
✔Lower financial risk– Reduces dependence on external creditors.✔Stable cash flow– Ensures business continuity during economic downturns.✔Better credit rating– Stronger financial health allows for lower borrowing costs if needed.
Disadvantages of Conservative Funding
❌Slower business growth– Limited access to capital can restrict expansion.❌Missed market opportunities– Competitors with aggressive funding may outpace the company.❌Higher cost of capital– Equity financing (selling shares) dilutes ownership and reduces profit per share.
????Best for:Established businesses, risk-averse industries, and companies focusing on long-term sustainability.
3. Comparison Table: Aggressive vs. Conservative Funding Approaches
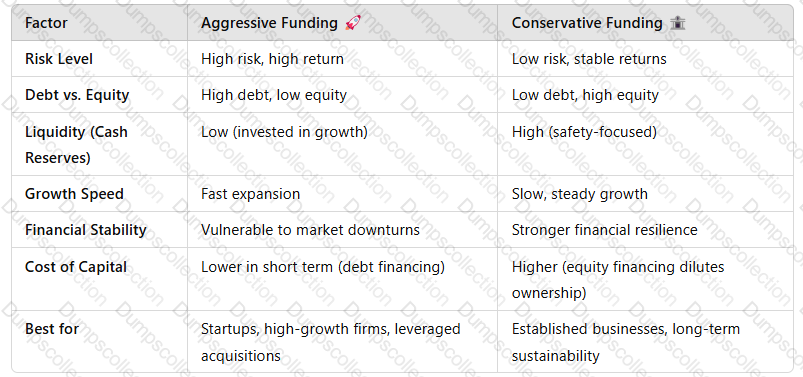 A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:The best funding approach depends onindustry, company stage, and risk appetite.
4. Which Approach Should a Business Use?
✅Aggressive Approach is Ideal For:
Startups & High-Growth Companies– Needfast capitalto capture market share.
Businesses in Competitive Markets– Companies that mustoutpace rivals through aggressive expansion.
Private Equity & Leveraged Buyouts– Maximizing returns throughhigh debt strategies.
✅Conservative Approach is Ideal For:
Mature & Stable Businesses– Companies prioritizingsteady revenue and financial security.
Family-Owned Enterprises– Owners preferlow debt and long-term growth.
Risk-Averse Industries– Businesses inessential goods/services sectorswherestability is more important than rapid expansion.
Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds?
????Many businesses use a combination of both approaches, leveragingdebt for growth while maintaining financial stabilitythrough retained earnings and equity.
????Example:
Appleused a conservative strategy in its early years but adoptedaggressive funding for global expansionpost-2010.
5. Conclusion
The choice betweenaggressive and conservative fundingdepends on a company’sgrowth goals, financial risk tolerance, and industry conditions.
✅Aggressive funding maximizes short-term growthbut increases financial risk.✅Conservative funding ensures stabilitybut limits expansion speed.✅Most companies use a hybrid modelto balancegrowth and financial security.
Understanding these approaches helps businessesoptimize capital structure, manage risk, and align financing with strategic objectives.
Discuss 4 stages of the industry and product lifecycle and explain how this can impact upon a company’s business strategy.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Industry and Product Lifecycle Stages & Their Impact on Business Strategy
Introduction
TheIndustry and Product Lifecycle Modeldescribes how industries and products evolve over time, affectingmarket demand, competition, and profitability. The model consists offour stages—Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline—each influencing a company’sstrategic decisions on marketing, pricing, production, and investment.
Companies mustadapt their business strategyat each stage to remain competitive, maximize profitability, and sustain long-term growth.
1. Four Stages of the Industry and Product Lifecycle
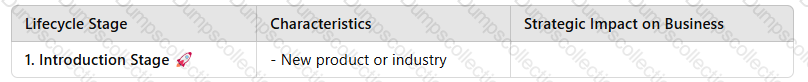
High R&D and marketing costs
Limited competition
Low sales volume | - High investment inproduct development & market awareness
Skimming or penetration pricingstrategy
Targetearly adopters& build brand identity | |2. Growth Stage????| - Rising sales & market demand
More competitors enter the market
Profitability increases
Scaling production | -Expand distribution & market reach
Enhance product differentiation
Increaseadvertising & brand positioning
Invest insupply chain efficiency| |3. Maturity Stage????| - Market saturation
Slower growth rate
Intense price competition
Peak profitability | -Cost-cutting & process optimization
Focus oncustomer loyalty & retention
Introducenew features & upgrades
Expand intonew markets| |4. Decline Stage????| - Market demand falls
Profit margins shrink
Product obsolescence
Competitor innovations take over | -Discontinue or rebrand the product
Shift tonew technology or innovation
Reduce production costs orexit the market|
2. Impact of Lifecycle Stages on Business Strategy
1. Introduction Stage – Market Entry Strategy????
Companies mustinvest heavilyinR&D, marketing, and infrastructureto introduce a new product or enter a new industry.
✅Strategic Decisions:
High R&D spending on innovation andpatent protection.
Pricing strategy:Eitherpremium pricing (skimming)for high-end customers orlow pricing (penetration)to gain market share quickly.
Targetearly adopters and niche customersto build brand awareness.
????Example:Tesla’sModel Slaunch in 2012 targeted early EV adopters, using ahigh-end pricing strategyto attract premium buyers.
2. Growth Stage – Expanding Market Share????
As demandincreases, companies mustscale operations, expand marketing, and stay ahead of competitors.
✅Strategic Decisions:
Expand intonew geographic marketsand increase production capacity.
Invest inadvertising and promotional campaignsto establish brand dominance.
Improveproduct differentiation(e.g., adding new features, improving design).
????Example:Apple’s iPhone growth strategyfocused on expanding intoemerging marketswhile continuously innovating hardware and software.
3. Maturity Stage – Maintaining Competitive Advantage????
Market saturation leads toslower growth, intense competition, and price wars. Companies mustfocus on cost efficiency and customer loyalty.
✅Strategic Decisions:
Implementcost-cutting measuresand optimize supply chains.
Shift focus tobrand loyalty programs and after-sales services.
Introduceproduct extensions, upgrades, or new modelsto sustain demand.
????Example:Coca-Colacontinues to dominate the mature soft drink market bylaunching new flavors (e.g., Coke Zero)and aggressive brand marketing.
4. Decline Stage – Managing Product or Market Exit????
When demand declines due tochanging consumer preferences or technological advancements, companies mustdecide whether to exit or reinvent the product.
✅Strategic Decisions:
Discontinue the productand shift focus to more profitable ventures.
Rebrand or repositionthe product to attract a niche market.
Diversify into new product categoriesto stay relevant.
????Example:Blockbuster failed to adaptin the decline stage, whereasNetflix transitioned from DVDs to streaming, ensuring survival.
Conclusion
TheIndustry and Product Lifecycle Modelguides companies in making strategic decisions at each stage. To succeed, businesses mustadapt their pricing, marketing, investment, and innovation strategiesaccordingly. Organizations thatfail to adjust(e.g., Kodak in digital photography) risk losing market relevance, while those thatinnovate and diversify(e.g., Netflix, Tesla) achieve long-term sustainability.
XYZ is a large technology organisation which has used an aggressive growth strategy to become the market leader. It frequently buys out smaller firms to add to its increasing portfolio of businesses. How could XYZ use the Kachru Parenting Matrix to assist in decision making regarding future investments?
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Using the Kachru Parenting Matrix for XYZ’s Investment Decisions
Introduction
TheKachru Parenting Matrixis astrategic decision-making toolthat helps businesses evaluate how well aparent company can add value to its subsidiaries. For XYZ, alarge technology firmthat follows anaggressive acquisition strategy, the Kachru Parenting Matrix can guide investment decisions byassessing the synergy between the parent company (XYZ) and its acquired businesses.
By using this matrix, XYZ can determine which acquisitions willbenefit from its expertise, resources, and management style, ensuring maximum strategic alignment and value creation.
1. Explanation of the Kachru Parenting Matrix
TheKachru Parenting Matrixevaluates business units based on:
Business Unit Fit– How well the subsidiary aligns with the parent company’score capabilities and expertise.
Parenting Advantage– The ability of the parent company toadd valueto the subsidiary through strategic oversight, resources, and expertise.
It categorizes business units intofour quadrants, influencing investment decisions:
|Parenting Advantage →
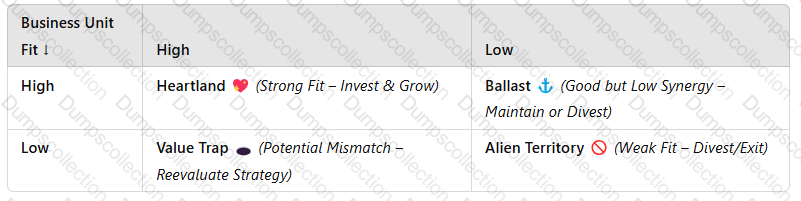 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
2. How XYZ Can Use the Kachru Parenting Matrix for Investment Decisions
1. Identifying Core Growth Areas – Heartland Businesses????(Invest & Grow)
These businessesstrongly alignwith XYZ’s expertise and benefit from itstechnology, resources, and leadership.
XYZ shouldprioritize investment, innovation, and expansionin these areas.
????Example:If XYZ specializes inAI and cloud computing, acquiringsmaller AI startupswould fall into theHeartlandcategory, ensuring seamless integration and value creation.
✅Strategic Action:Invest inR&D, talent acquisition, and global expansionfor these subsidiaries.
2. Maintaining Complementary Businesses – Ballast Businesses⚓(Maintain or Divest if Needed)
These businesses areprofitable but do not directly fit XYZ’s core strategy.
XYZ cankeep them for financial stabilityor sell them if theydrain management resources.
????Example:If XYZ acquires ahardware companybut primarily operates insoftware, the hardware unit maynot fully align with its expertise.
✅Strategic Action:Maintain for profitabilityor sell if it becomes a burden.
3. Avoiding Value Draining Investments – Value Trap Businesses????️(Reevaluate or Divest)
These businessesseem promising but struggle under XYZ’s management approach.
They may requiretoo much intervention, reducing overall profitability.
????Example:If XYZ buysa social media companybut lacks the right expertise to monetize it effectively, itbecomes a value trap.
✅Strategic Action:Reevaluateif restructuring is possible; otherwise,sellto avoid financial losses.
4. Exiting Poorly Aligned Businesses – Alien Territory????(Divest Immediately)
These businessesdo not align at allwith XYZ’s strategy or expertise.
Keeping them leads toresource misallocation and inefficiencies.
????Example:If XYZ acquiresa retail clothing company, it would be inAlien Territory, as it does not fit within thetechnology industry.
✅Strategic Action:Divest or spin offthese businesses to focus on core competencies.
3. Strategic Benefits of Using the Kachru Parenting Matrix
✅Improves Investment Focus– Helps XYZidentify the most valuable acquisitions.✅Enhances Synergy & Value Creation– Ensuressubsidiaries benefit from XYZ’s resources and leadership.✅Prevents Poor Acquisitions– Avoidswasting capital on unrelated businesses.✅Optimizes Portfolio Management– Balanceshigh-growth and stable revenue businesses.
4. Conclusion
TheKachru Parenting Matrixis acritical toolfor XYZ to assessfuture acquisitions, ensuring that each business unit contributes tolong-term profitability and strategic alignment.
✅Heartland businessesshould receivemaximum investment.✅Ballast businessescan be maintainedfor financial stability.✅Value Trap businessesshould bereevaluated or restructured.✅Alien Territory businessesmust bedivested to avoid inefficiencies.
By using this framework, XYZ can ensuresmarter, more strategic acquisitions, maintaining itsmarket leadershipwhileavoiding financial risks.
XYZ is a successful cake manufacturer and wishes to expand the business to create additional confectionary items. The expansion will require the purchase of a further manufacturing facility, investment in machinery and the hiring of more staff. The CEO and CFO are confident that the diversification will be a success and are discussing ways to raise funding for the expansion and are debating between dept funding and funding.What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of Debt Funding vs. Equity Funding for XYZ’s Expansion
Introduction
As XYZ, a successfulcake manufacturer, plans to expand intoadditional confectionery items, it requires significant investment ina new manufacturing facility, machinery, and staff. To finance this expansion, the company must choose between:
Debt Funding– Borrowing from banks or financial institutions.
Equity Funding– Raising capital by selling shares to investors.
Each funding option hasadvantages and disadvantagesthat impactfinancial stability, ownership control, and long-term business strategy.
1. Debt Funding????(Loans, Bonds, or Credit Facilities)
Definition
Debt funding involvesborrowing moneyfrom banks, lenders, or issuing corporate bonds, which must be repaid with interest.
✅Key Characteristics:
The company retainsfull ownership and decision-making control.
Loan repayments are fixed and predictable.
Interest payments aretax-deductible.
????Example:XYZ takes abank loan of £2 millionto purchase new machinery and repay it over five years with interest.
Advantages of Debt Funding
✔Ownership Retention– XYZ keeps full control over business decisions.✔Predictable Repayment Plan– Fixed monthly payments make financial planning easier.✔Tax Benefits– Interest paymentsreduce taxable income.✔Shorter-Term Obligation– Once the loan is repaid, there are no further obligations.
Disadvantages of Debt Funding
❌Repayment Pressure– Regular repaymentsincrease financial riskduring slow sales periods.❌Interest Costs– High-interest rates canreduce profitability.❌Collateral Requirement– Lenders may requirecompany assets as security.❌Credit Risk– If XYZ fails to repay, it riskslosing assets or damaging credit ratings.
????Best for:Companies that want tomaintain ownership and have stable revenue streamsto cover repayments.
2. Equity Funding????(Selling Shares to Investors or Venture Capitalists)
Definition
Equity funding involvesraising capital by selling sharesin the company to investors, such asprivate investors, venture capitalists, or the stock market.
✅Key Characteristics:
No repayment obligations, but shareholders expect areturn on investment (ROI).
Investorsgain partial ownershipand may influence business decisions.
Funding amount depends on the company’svaluation and investor interest.
????Example:XYZ sells20% of its shares to a private investor for £3 million, which funds new production lines.
Advantages of Equity Funding
✔No Repayment Obligation– Reduces financial burden on cash flow.✔Access to Large Capital– Easier to raise significant funds for expansion.✔Attracts Strategic Investors– Investors may provide expertise and industry connections.✔Spreads Business Risk– Losses are shared with investors, reducing pressure on XYZ.
Disadvantages of Equity Funding
❌Loss of Ownership & Control– Investors gain a say in company decisions.❌Profit Sharing– Dividends or profit-sharing reduce earnings for existing owners.❌Longer Decision-Making Process– Raising equity capital takes time due to negotiations and regulatory compliance.❌Dilution of Shares– Selling shares reduces the founder’s ownership percentage.
????Best for:Companies needinglarge funding amounts with less repayment pressure, but willing toshare ownership and decision-making.
3. Comparison: Debt vs. Equity Funding
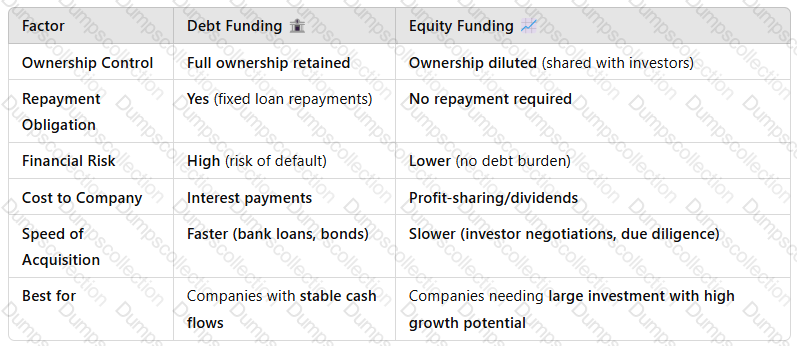 A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:The choice betweendebt and equity fundingdepends on XYZ’srisk tolerance, cash flow stability, and long-term growth strategy.
4. Conclusion & Recommendation
Bothdebt funding and equity fundingoffer advantages and risks for XYZ’s expansion.
✅Debt fundingis ideal if XYZ wants toretain ownership and has stable revenueto cover loan repayments.✅Equity fundingis better if XYZ seekslarger investments, strategic expertise, and reduced financial risk.
????Recommended Approach:Ahybrid strategy, combiningdebt for short-term capital needsandequity for long-term growth, can providefinancial flexibility while minimizing risks.
XYZ is a manufacturing company based in the UK. It has a large complex supply chain and imports raw materials from Argentina and South Africa. It sells completed products internationally via their website. Evaluate the role of licencing and taxation on XYZ’s operations.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of the Role of Licensing and Taxation on XYZ’s Operations
Introduction
Licensing and taxation play acritical role in international trade, supply chain management, and overall financial performance. For XYZ, aUK-based manufacturing companythat importsraw materials from Argentina and South Africaand sellsinternationally via an e-commerce platform, compliance with licensing and taxation regulations is essential to ensuresmooth operations, cost efficiency, and legal compliance.
This evaluation will assess theimpact of licensing and taxation on XYZ’s global supply chain, import/export activities, and financial performance.
1. The Role of Licensing in XYZ’s Operations
1.1 Import and Export Licensing Regulations
As XYZ importsraw materials from Argentina and South Africa, it must comply with theUK’s import licensing requirementsand trade agreements with these countries.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Import licensesmay be required for certain restricted raw materials (e.g.,metals, chemicals, agricultural products).
Export control lawsmay apply, depending on thedestination of final products.
Delays or finesmay occur if licenses are not properly managed.
????Example:If XYZ importsmetal componentssubject to UK trade restrictions, it mustsecure import licensesbefore shipment clearance.
1.2 Industry-Specific Licensing Requirements
Some industries requirespecial licensesto manufacture and sell products globally.
✅Impact on XYZ:
If XYZ manufactureselectronics or chemical-based products, it may need compliance certifications (e.g.,CE marking in the EU, FDA approval in the US).
Failure to meet licensing requirements canblock international sales.
????Example:A UK manufacturer sellingmedical devicesmust obtainMHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency) approvalbefore distributing products.
1.3 E-Commerce & Digital Sales Licensing
As XYZ sells its products internationally via itswebsite, it must comply with:✅Consumer Protection Laws(e.g., GDPR for EU customers).✅E-commerce business registrationand online sales regulations.
????Example:XYZ may need aVAT number in the EUif it sells products to European customers via its website.
2. The Role of Taxation in XYZ’s Operations
2.1 Import Duties and Tariffs
XYZ’s supply chain involvesimporting raw materials from Argentina and South Africa, which may attractimport duties and tariffs.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Higherimport duties increase raw material costsand impact profitability.
Tariff-free trade agreements(e.g., UK-South Africa trade deal)may reduce costs.
Post-Brexit UK-EU trade regulationsmay affect supply chain tax structures.
????Example:If theUK imposes high tariffs on South African goods, XYZ may need tofind alternative suppliers or negotiate better deals.
2.2 Corporate Tax & International Tax Compliance
XYZ must comply withUK corporate tax lawsand international taxation regulations.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Payingcorporate tax in the UKbased onglobal sales revenue.
Managinginternational tax obligationswhen selling in multiple countries.
Risk of double taxationif the same income is taxed in multiple jurisdictions.
????Example:If XYZ sells products inGermany and the US, it may need toregister for tax in those countriesand comply withlocal VAT/GST requirements.
2.3 Value Added Tax (VAT) & Sales Tax
Since XYZsells internationally via its website, it must adhere toglobal VAT and sales tax rules.
✅Impact on XYZ:
In theEU, VAT registration is required for online sales above a certain threshold.
In theUS, sales tax regulations varyby state.
Compliance withUK VAT laws (e.g., 20% standard rate)on domestic sales.
????Example:A UK company sellingonline to EU customersmust comply with theEU One-Stop-Shop (OSS) VAT scheme.
2.4 Transfer Pricing & Tax Efficiency
If XYZhas international subsidiaries or supply chain partners, it must managetransfer pricing regulations.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Ensuringfair pricing between UK operations and overseas supplierstoavoid tax penalties.
Optimizingtax-efficient supply chain structurestominimize tax burdens.
????Example:Multinational companies likeApple and Amazonusetax-efficient structuresto reduce liabilities.
3. Strategic Actions for XYZ to Manage Licensing and Taxation Effectively
XYZ can take several steps tooptimize tax compliance and licensing efficiency:
 A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
Conclusion
Licensing and taxation have amajor impact on XYZ’s international manufacturing and e-commerce operations. To maintain profitability andregulatory compliance, XYZ must:
✅Ensureimport/export licensingaligns with UK and international trade laws.✅Manageimport duties, VAT, and corporate tax obligationseffectively.✅Optimize itssupply chain and tax planningto reduce costs.
By proactively managing these areas, XYZ canenhance its global competitiveness while minimizing risks.
Explain, with examples, why supply and demand fluctuate in the commodities market
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Why Supply and Demand Fluctuate in the Commodities Market
Introduction
Thecommodities marketis highly volatile, with prices and availability constantly influenced byfluctuations in supply and demand. These fluctuations arise due to factors such asclimate conditions, geopolitical events, economic cycles, and technological advancements.
Understandingwhy supply and demand shifthelps businesses, investors, and policymakersanticipate market trends and mitigate risks.
1. Factors Affecting Supply in the Commodities Market
1.1 Weather and Climate Conditions☀️????️(Impact on Agricultural Commodities)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Droughts, floods, hurricanes, or frostscan damage crops, reducing supply.
Favorable weather leads tohigher yields and increased supply.
????Example:
In2019, severe droughts in Australiareduced wheat production, increasing global wheat prices.
Astrong coffee harvest in Brazilled tohigher supply and lower coffee prices.
????Key Takeaway:Agricultural commodity supply ishighly dependent on weather variability.
1.2 Geopolitical Events and Trade Restrictions????️????(Impact on Energy & Metals)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Political instability, sanctions, and warsdisrupt supply chains.
Trade policies, tariffs, and embargoesrestrict exports/imports.
????Example:
Russia-Ukraine war (2022)led to amajor disruption in wheat and oil exports, causing global shortages.
US-China trade tensionsaffected theavailability of rare earth metalsused in electronics.
????Key Takeaway:Supply chains inenergy, metals, and food commoditiesare vulnerable togeopolitical risks.
1.3 Production Costs & Technological Advancements⚙️????(Impact on Oil, Metals, and Agricultural Goods)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Higher production costs (e.g.,fuel, labor, mining operations)reduce supply.
New technologies improve extraction and farming efficiency,increasing supply.
????Example:
Shale oil extraction technology in the USincreased crude oil supply, leading to lower global oil prices.
Higher fertilizer costs in 2023led to reduced crop production in some countries.
????Key Takeaway:Technological advancements increase supply, while rising production costs limit it.
2. Factors Affecting Demand in the Commodities Market
2.1 Economic Growth & Industrial Demand????????(Impact on Oil, Metals, and Construction Materials)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Economic booms drive higher demand foroil, metals, and raw materials.
During recessions, demand for industrial commoditiesfalls.
????Example:
China’s rapid industrialization (2000s)increased demand foriron ore, copper, and coal, pushing prices up.
COVID-19 lockdowns (2020)caused a sharp drop inoil demand, leading to negative oil prices in April 2020.
????Key Takeaway:Commodity demandrises during economic expansion and falls during downturns.
2.2 Changing Consumer Preferences & Market Trends????️????(Impact on Food & Energy Commodities)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Shifts in diet, lifestyle, and energy useaffect commodity demand.
Green energy transitionsreduce fossil fuel demandbut increase demand for alternative materials.
????Example:
Increased veganism in Western marketsboosted demand forsoybeans, almonds, and plant-based protein.
Electric vehicle (EV) adoptionincreased demand forlithium, cobalt, and nickelused in EV batteries.
????Key Takeaway:Demand changes due toconsumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability trends.
2.3 Speculation & Investment Activity????????(Impact on Gold, Oil, and Agricultural Commodities)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Investors and hedge fundsbuy commodities as a hedge against inflation or currency fluctuations.
Speculative tradingincreases volatility, driving short-term price spikes.
????Example:
Gold prices surge during economic crisesas investors seek a safe-haven asset.
Oil price spikes in 2008 and 2022were partly due tospeculative trading.
????Key Takeaway:Commodity demand isinfluenced by financial markets and speculation.
3. How Supply & Demand Interact to Affect Prices
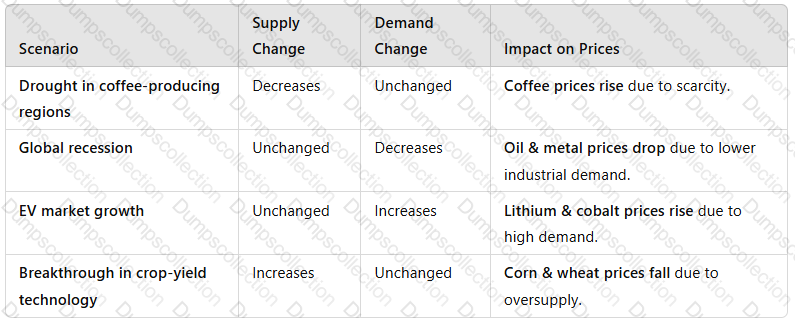 A white grid with black text
Description automatically generated
A white grid with black text
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:Prices aredetermined by the balance between supply availability and consumer demand.
4. Conclusion
The commodities market experiencesconstant fluctuations in supply and demand, driven by:
✅Weather & Climate– Affects agricultural output.✅Geopolitical & Trade Issues– Disrupts supply chains.✅Economic Cycles & Industrial Growth– Determines demand levels.✅Consumer Preferences & Technological Trends– Changes demand patterns.✅Speculation & Investor Activity– Influences short-term price volatility.
Understanding these factors allows businesses toforecast commodity price movements, manage procurement risks, and optimize supply chain strategies.
XYZ is a toilet paper manufacturer based in the UK. It has 2 large factories employing over 500 staff and a complex supply chain sourcing paper from different forests around the world. XYZ is making some strategic changes to the way it operates including changes to staffing structure and introducing more automation. Discuss 4 causes of resistance to change that staff at XYZ may experience and examine how the CEO of XYZ can successfully manage this resistance to change
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Causes of Resistance to Change & Strategies to Manage It – XYZ Case Study
When XYZ, a UK-based toilet paper manufacturer, implementsstrategic changessuch asstaff restructuring and automation, employees mayresist changedue to uncertainty, fear, and disruption to their work environment. Below arefour key causes of resistanceand how theCEO can manage them effectively.
Causes of Resistance to Change
1. Fear of Job Loss
????Cause:Employees may fear thatautomationwill replace their jobs, leading to layoffs. Factory workers and administrative staff may feel particularly vulnerable.
????Example:If machines take over manual processes like paper cutting and packaging, employees may see this as a direct threat to their roles.
2. Lack of Communication and Transparency
????Cause:When managementfails to communicatethe reasons for change, employees may speculate and assume the worst.Unclear messageslead to distrust.
????Example:If XYZ’s CEO announces restructuring without explainingwhyandhowjobs will be affected, employees may feel insecure and disengaged.
3. Loss of Skills and Status
????Cause:Some employees, especiallylong-serving workers, may feel their skills are becoming obsolete due to automation.Managersmay resist change if they fear losing power in a new structure.
????Example:A production line supervisor mayoppose automationbecause it reduces the need for human oversight, making their role seem redundant.
4. Organizational Culture and Habit
????Cause:Employees are accustomed tospecific ways of working, andsudden changes disrupt routine. Resistance occurs when changes challengeexisting work culture.
????Example:XYZ’s employees may havealways used manual processes, and shifting toAI-driven productionfeels unfamiliar and uncomfortable.
How the CEO Can Manage Resistance to Change
1. Effective Communication Strategy
✅What to do?
Clearly explainwhy the changes are necessary(e.g., cost efficiency, competitiveness).
Usetown hall meetings, emails, and team discussionsto provide updates.
Addressemployee concernsdirectly to reduce uncertainty.
????Example:The CEO can sendmonthly updateson automation, ensuring transparency and reducing fear.
2. Employee Involvement and Engagement
✅What to do?
Involve staff indecision-makingto give them a sense of control.
Createcross-functional teamsto gather employee input.
Provide opportunities forfeedback and discussion.
????Example:XYZ canform a worker’s advisory panelto gather employee concerns and address them proactively.
3. Training and Upskilling Programs
✅What to do?
Offertraining programsto help employees adapt to new technologies.
Providereskilling opportunitiesfor employees whose jobs are affected.
Reassure staff that automation willcreate new roles, not just eliminate jobs.
????Example:XYZ can introducedigital skills trainingfor workers transitioning from manual processes to automated systems.
4. Change Champions & Support Systems
✅What to do?
Appointchange champions(influential employees) to advocate for change.
Offeremotional and psychological support(e.g., HR consultations, career guidance).
Recognize and reward employees whoembrace change.
????Example:XYZ can offerbonuses or promotionsto employees who successfully transition into new roles.
Conclusion
Resistance to change is natural, but theCEO of XYZ can minimize resistancethroughclear communication, employee involvement, training, and structured support. By managing resistance effectively, XYZ can ensure asmooth transitionwhile maintaining employee morale and operational efficiency.
Discuss the following strategic decisions, explaining the advantages and constraints of each: Market Penetration, Product Development and Market Development.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of Strategic Decisions: Market Penetration, Product Development, and Market Development
Introduction
Strategic decisions in business involve selecting the best approach togrow market share, increase revenue, and sustain competitive advantage. According toAnsoff’s Growth Matrix, businesses can pursuefour strategic directions:
Market Penetration(expanding sales in existing markets with existing products)
Product Development(introducing new products to existing markets)
Market Development(expanding into new markets with existing products)
Diversification(introducing new products to new markets)
This answer focuses onMarket Penetration, Product Development, and Market Development, discussingtheir advantages and constraints.
1. Market Penetration????(Increasing sales of existing products in existing markets)
Explanation
Market penetration involves increasing market share by:✅Encouraging existing customers to buy more.✅Attracting competitors’customers.✅Increasing promotional efforts.✅Improving pricing strategies.
????Example:Coca-Cola usesaggressive marketing, promotions, and pricing strategiesto increase sales in existing markets.
Advantages of Market Penetration
✔Low Risk– No need for new product development.✔Cost-Effective– Uses existing infrastructure and supply chain.✔Builds Market Leadership– Strengthens brand loyalty and customer retention.✔Quick Revenue Growth– Increased sales generate higher profits.
Constraints of Market Penetration
❌Market Saturation– Limited growth potential if the market is already saturated.❌Intense Competition– Competitors may retaliate with price cuts and promotions.❌Diminishing Returns– Lowering prices to attract customers can reduce profitability.
????Strategic Consideration:Businesses should assesscustomer demand and competitive intensitybefore implementing a market penetration strategy.
2. Product Development????(Introducing new products to existing markets)
Explanation
Product development involves launchingnew or improved productsto meet evolving customer needs. This can include:✅Innovation– Developing new features or technology.✅Product Line Extensions– Introducing variations (e.g., new flavors, models, packaging).✅Customization– Tailoring products to specific customer preferences.
????Example:Apple frequently launchesnew iPhone modelsto attract existing customers.
Advantages of Product Development
✔Higher Customer Retention– Keeps existing customers engaged with new offerings.✔Brand Differentiation– Strengthens competitive advantage through innovation.✔Increases Revenue Streams– Expands product portfolio and market opportunities.
Constraints of Product Development
❌High R&D Costs– Requires investment in innovation and testing.❌Market Uncertainty– New products may fail if not aligned with customer needs.❌Risk of Cannibalization– New products may reduce sales of existing products.
????Strategic Consideration:Businesses should conductmarket research, prototyping, and feasibility analysisbefore launching new products.
3. Market Development????(Expanding into new markets with existing products)
Explanation
Market development involvesselling existing products in new geographical areas or customer segments. Strategies include:✅Expanding into international markets.✅Targeting new demographics (e.g., different age groups or industries).✅Entering new distribution channels (e.g., e-commerce, retail stores).
????Example:McDonald’s expands intonew countries, adapting its menu to local preferences.
Advantages of Market Development
✔Access to New Revenue Streams– Increases customer base and sales.✔Diversifies Market Risk– Reduces dependency on a single region.✔Leverages Existing Products– No need for costly product innovation.
Constraints of Market Development
❌Cultural and Regulatory Barriers– Differences in consumer behavior, legal requirements, and competition.❌High Entry Costs– Requires investment inmarketing, distribution, and local partnerships.❌Operational Challenges– Managing supply chains and logistics in new markets.
????Strategic Consideration:Businesses should conductmarket analysis and risk assessmentsbefore expanding internationally.
Conclusion
Each strategic decision hasunique benefits and challenges:
✅Market Penetrationislow-riskbutlimited by market saturation.✅Product Developmentdrivesinnovationbut requireshigh investment.✅Market Developmentexpands revenue streamsbut involvescultural and regulatory challenges.
The best approach depends on a company’scompetitive position, financial resources, and long-term growth objectives.
Organisations in the private sector often need to make decisions regarding financing, investment and dividends.Discuss factors that affect these decisions.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Factors Affecting Financing, Investment, and Dividend Decisions in Private Sector Organizations
Introduction
Private sector organizations must carefully balancefinancing, investment, and dividend decisionsto ensurefinancial stability, profitability, and shareholder satisfaction. These decisions are influenced byinternal financial health, external economic conditions, market competition, and regulatory requirements.
This answer examines thekey factors affecting financing, investment, and dividend policiesin private sector companies.
1. Factors Affecting Financing Decisions????(How Companies Raise Capital?)
Financing decisionsdetermine how businessesfund operations, expansion, and debt repayment.
1.1 Cost of Capital????(Debt vs. Equity Considerations)
✅Why It Matters?
Companies choose betweendebt financing (bank loans, bonds)andequity financing (selling shares)based on thecost of capital.
Higher interest ratesmake debt financing expensive, while equity financing dilutes ownership.
????Example:
A startup may prefer equity financingto avoid immediate debt repayments.
A profitable company may use debtdue totax advantages on interest payments.
????Key Takeaway:Companies aim tominimize capital costswhile maintaining financial flexibility.
1.2 Company’s Creditworthiness & Risk Tolerance⚖️
✅Why It Matters?
Stronger credit ratingsallow companies to secure loans atlower interest rates.
Riskier businesses maystruggle to secure financingor facehigh borrowing costs.
????Example:
Apple can easily issue corporate bondsdue to its strong financial position.
A high-risk startup may have to offer higher interest rateson its debt.
????Key Takeaway:Financially stable firms havemore funding options at lower costs.
1.3 Economic Conditions????(Market Trends & Inflation)
✅Why It Matters?
Ineconomic downturns, companies avoid excessive borrowing.
Inflation and interest rate hikesincrease financing costs.
????Example:
Duringrecessions, companies reduce borrowing to avoidhigh debt risks.
In abooming economy, firms take loans toexpand production and capture market share.
????Key Takeaway:Businesses adjust financing strategies based oneconomic stability and interest rates.
2. Factors Affecting Investment Decisions????(Where and How Companies Invest Capital?)
2.1 Expected Return on Investment (ROI)????
✅Why It Matters?
Companies evaluate potentialprofits from investmentsbefore committing capital.
High-ROI projects are prioritized, while low-ROI investments are avoided.
????Example:
Tesla invests in battery technologydue to high future demand.
A retail chain avoids investing in struggling marketswith low profitability.
????Key Takeaway:Businesses prioritizehigh-return investmentsthat align with strategic goals.
2.2 Risk Assessment & Diversification????
✅Why It Matters?
Companies assessmarket, operational, and financial risksbefore investing.
Diversification reduces reliance on asingle revenue source.
????Example:
Amazon diversified into cloud computing (AWS)to reduce dependence on e-commerce sales.
Oil companies invest in renewable energyto hedge against declining fossil fuel demand.
????Key Takeaway:Investment decisions focus onbalancing risk and opportunity.
2.3 Availability of Internal Funds vs. External Borrowing????
✅Why It Matters?
Companies useretained earningswhen available toavoid debt costs.
When internal funds are insufficient, theyborrow or raise equity capital.
????Example:
Google reinvests profits into AI and software developmentinstead of taking loans.
A new airline expansionmay requiredebt financing for aircraft purchases.
????Key Takeaway:Investment decisions depend onfund availability and cost considerations.
3. Factors Affecting Dividend Decisions????(How Companies Distribute Profits to Shareholders?)
3.1 Profitability & Cash Flow Stability????
✅Why It Matters?
Profitable companiespay higher dividends, while struggling firms reduce payouts.
Strong cash flow ensuresconsistent dividend payments.
????Example:
Microsoft pays regular dividendsdue to itssteady revenue stream.
A startup reinvests all profitsinto business growth instead of paying dividends.
????Key Takeaway:Onlyprofitable, cash-rich companiessustain high dividend payouts.
3.2 Growth vs. Payout Trade-Off????
✅Why It Matters?
High-growth firmsreinvest profitsfor expansion instead of paying high dividends.
Mature companies withstable profitsfocus on rewarding shareholders.
????Example:
Amazon reinvests heavily in logistics and AIrather than paying high dividends.
Coca-Cola pays consistent dividendsas its industry growth is slower.
????Key Takeaway:Companies balancegrowth investment and shareholder returns.
3.3 Shareholder Expectations & Market Perception????
✅Why It Matters?
Investors expect dividends, especially inblue-chip and income-focused stocks.
Suddendividend cutscan signalfinancial trouble, affecting share prices.
????Example:
Unilever maintains stable dividendsto attract income-focused investors.
Tesla does not pay dividends, focusing on long-term growth and innovation.
????Key Takeaway:Dividend policies affectinvestor confidence and stock valuation.
4. Summary: Key Factors Influencing Financial Decisions
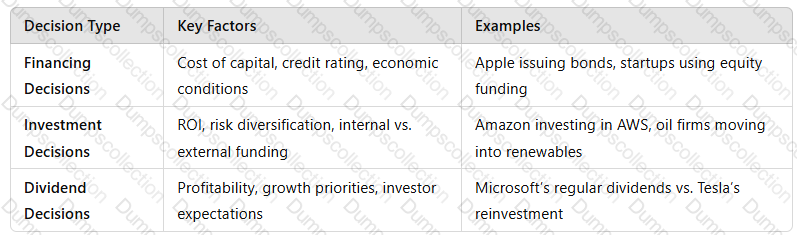 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:Companiesbalance financing, investment, and dividend decisionsbased onprofitability, risk assessment, and market conditions.
5. Conclusion
Private sector companies makestrategic financial decisionsby evaluating:
✅Financing Needs:Debt vs. equity, cost of borrowing, and risk management.✅Investment Priorities:Expected ROI, business growth, and market opportunities.✅Dividend Strategy:Balancing shareholder returns and reinvestment for growth.
Understanding these factors helps businessesmaximize financial performance, shareholder value, and long-term sustainability.
Evaluate the role of strategic human management in creating competitive advantage for an organisation
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of the Role of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) in Creating Competitive Advantage
Introduction
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is theproactive alignment of HR policies withbusiness strategyto achieve long-term success. It focuses on developingtalent, leadership, culture, and employee engagementto enhanceorganizational performance and competitiveness.
By implementingeffective SHRM practices, companies can create asustainable competitive advantagethrough a highly skilled and motivated workforce.
1. The Role of SHRM in Creating Competitive Advantage
1.1 Talent Acquisition and Workforce Planning
✅Why it matters?
Recruiting and retaininghighly skilled employeesis essential for innovation and efficiency.
Workforce planning ensuresthe right people are in the right rolesat the right time.
????Example:Google’s strategic hiring approachfocuses on attractingtop AI and engineering talent, driving innovation in tech.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Builds anexpert workforcethat competitors cannot easily replicate.✔Reducesturnover costsby ensuring long-term retention.
1.2 Employee Development and Training
✅Why it matters?
Continuous learning and skills development enhanceemployee productivity and innovation.
Upskilling employees keeps companies ahead infast-changing industries.
????Example:Amazon’s Career Choice Programinvests in employee training to develop future leaders and improve workforce capabilities.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Enhances organizational agilityby equipping employees withemerging skills.✔Creates a culture ofcontinuous improvement and innovation.
1.3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement
✅Why it matters?
Effective performance management systemsensure employees align with business goals.
Engaged employees aremore productive, motivated, and committedto company success.
????Example:Salesforce’s focus on employee engagementthrough leadership development and internal career growth has resulted in high retention and innovation.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Driveshigh workforce productivityand efficiency.✔Reduces costs related topoor performance and disengagement.
1.4 HR Technology and Data-Driven Decision-Making
✅Why it matters?
Digital HR tools (e.g.,AI-driven recruitment, performance analytics, HR automation) optimize talent management.
Data-driven HR strategies help predictworkforce trends and talent gaps.
????Example:Unilever uses AI-driven HR analyticsto identify high-potential employees and enhance leadership succession planning.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Enablesdata-driven workforce planningfor future growth.✔Increasesefficiency and reduces hiring biases.
1.5 Employee Well-being and Diversity & Inclusion
✅Why it matters?
Work-life balance policies, mental health support, and DEI (Diversity, Equity, Inclusion) programsimprove workplace culture.
Diverse teamsenhance creativity, problem-solving, and innovation.
????Example:Microsoft’s Diversity & Inclusion programshave strengthened its brand and innovation by fostering amore inclusive workforce.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Attractstop global talentwho seek inclusive workplaces.✔Strengthensbrand reputation and employee loyalty.
2. Advantages of Strategic HRM in Competitive Positioning
✅Develops Unique Talent & Expertise– Hard for competitors to replicate.✅Enhances Productivity & Efficiency– Skilled, engaged employees drive better results.✅Supports Business Agility & Innovation– Workforce is adaptable to market changes.✅Builds Strong Employer Brand– Attracts and retains high-quality talent.
????Key Takeaway:SHRM transformsHR from an administrative function to a strategic assetthat creates long-term value.
3. Challenges & Risks of SHRM
❌Implementation Costs– Advanced HR technology and training require investment.❌Resistance to Change– Employees may resist new HR policies.❌Measuring ROI Can Be Complex– Talent development impacts long-term but ishard to quantify.❌Legal & Compliance Risks– Global HR policies mustalign with labor lawsacross different countries.
????Solution:Businesses must integrateHR analytics, leadership buy-in, and cultural change strategiesto overcome these challenges.
4. Conclusion
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) isa key driver of sustainable competitive advantageby:
✅Attracting and retaining top talent.✅Developing a highly skilled, engaged, and innovative workforce.✅Leveraging HR technology and data-driven insights.✅Promoting employee well-being, diversity, and inclusion.
Companies thatprioritize SHRMcreate adynamic, future-ready workforce, ensuring long-term success in competitive markets.

