GAQM Certified Professional Ethical Hacker (CPEH) CPEH-001 Exam Dumps: Updated Questions & Answers (March 2026)
You are monitoring the network of your organizations. You notice that:
1. There are huge outbound connections from your Internal Network to External IPs.
2. On further investigation, you see that the External IPs are blacklisted.
3. Some connections are accepted, and some are dropped.
4. You find that it is a CnC communication.
Which of the following solution will you suggest?
Which of the following DoS tools is used to attack target web applications by starvation of available sessions on the web server?
The tool keeps sessions at halt using never-ending POST transmissions and sending an arbitrarily large content-length header value.
Which of the following act requires employer’s standard national numbers to identify them on standard transactions?
An attacker scans a host with the below command. Which three flags are set? (Choose three.)
#nmap –sX host.domain.com
What is the least important information when you analyze a public IP address in a security alert?
Fred is the network administrator for his company. Fred is testing an internal switch.
From an external IP address, Fred wants to try and trick this switch into thinking it already has established a session with his computer. How can Fred accomplish this?
What kind of detection techniques is being used in antivirus softwares that identifies malware by collecting data from multiple protected systems and instead of analyzing files locally it's made on the premiers environment-
OpenSSL on Linux servers includes a command line tool for testing TLS. What is the name of the tool and the correct syntax to connect to a web server?
Let's imagine three companies (A, B and C), all competing in a challenging global environment. Company A and B are working together in developing a product that will generate a major competitive advantage for them. Company A has a secure DNS server while company B has a DNS server vulnerable to spoofing. With a spoofing attack on the DNS server of company B, company C gains access to outgoing e-mails from company B. How do you prevent DNS spoofing?
Under what conditions does a secondary name server request a zone transfer from a primary name server?
You are performing a penetration test for a client and have gained shell access to a Windows machine on the internal network. You intend to retrieve all DNS records for the internal domain, if the DNS server is at 192.168.10.2 and the domain name is abccorp.local, what command would you type at the nslookup prompt to attempt a zone transfer?
One of your team members has asked you to analyze the following SOA record. What is the version?
Rutgers.edu.SOA NS1.Rutgers.edu ipad.college.edu (200302028 3600 3600 604800 2400.) (Choose four.)
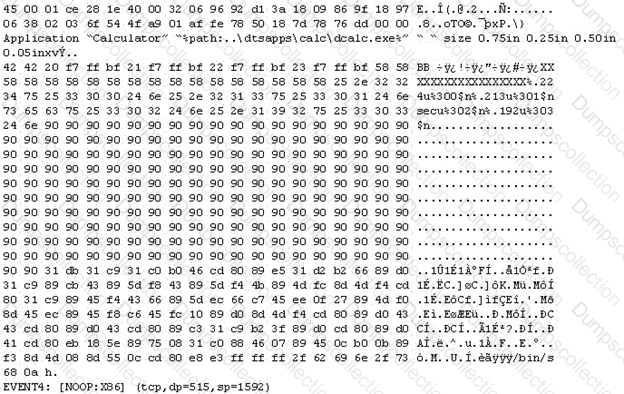
The following is an entry captured by a network IDS. You are assigned the task of analyzing this entry. You notice the value 0x90, which is the most common NOOP instruction for the Intel processor. You figure that the attacker is attempting a buffer overflow attack.
You also notice "/bin/sh" in the ASCII part of the output.
As an analyst what would you conclude about the attack?
What is GINA?
How does a denial-of-service attack work?

