Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) CKS Exam Dumps: Updated Questions & Answers (March 2026)
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may
result in a zero score.
[candidato@base] $ ssh cks000023
Task
Analyze and edit the Dockerfile located at /home/candidate/subtle-bee/build/Dockerfile, fixing one instruction present in the file that is a prominent security/best-practice issue.
Do not add or remove instructions; only modify the one existing instruction with a security/best-practice concern.
Do not build the Dockerfile, Failure to do so may result in running out of storage and a zero score.
Analyze and edit the given manifest file /home/candidate/subtle-bee/deployment.yaml, fixing one fields present in the file that are a prominent security/best-practice issue.
Do not add or remove fields; only modify the one existing field with a security/best-practice concern.
Should you need an unprivileged user for any of the tasks, use user nobody with user ID 65535.
Secrets stored in the etcd is not secure at rest, you can use the etcdctl command utility to find the secret value
for e.g:-
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get /registry/secrets/default/cks-secret --cacert="ca.crt" --cert="server.crt" --key="server.key"
Output
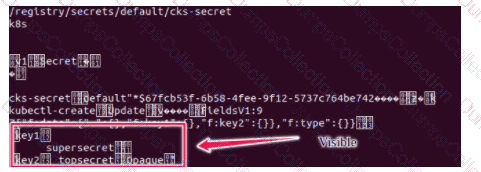
Using the Encryption Configuration, Create the manifest, which secures the resource secrets using the provider AES-CBC and identity, to encrypt the secret-data at rest and ensure all secrets are encrypted with the new configuration.
Use the kubesec docker images to scan the given YAML manifest, edit and apply the advised changes, and passed with a score of 4 points.
kubesec-test.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: kubesec-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: kubesec-demo
image: gcr.io/google-samples/node-hello:1.0
securityContext:
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
Hint: docker run -i kubesec/kubesec:512c5e0 scan /dev/stdin < kubesec-test.yaml
Documentation
Deployment, Pod Security Admission, Pod Security Standards
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000036
Context
For compliance, all user namespaces enforce the restricted Pod Security Standard .
Task
The confidential namespace contains a Deployment that is not compliant with the restricted Pod Security Standard . Thus, its Pods can not be scheduled.
Modify the Deployment to be compliant and verify that the Pods are running.
The Deployment's manifest file can be found at /home/candidate/nginx-unprivileged.yaml.
Documentation dockerd
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000037
Task
Perform the following tasks to secure the cluster node cks000037 :
Remove user developer from the docker group.
Do not remove the user from any other group.
Reconfigure and restart the Docker daemon to ensure that the socket
file located at /var/run/docker.sock is owned by the group root.
Re-configure and restart the Docker daemon to ensure it does not listen on any TCP port.
After completing your work, ensure the Kubernetes cluster is healthy.
Documentation Ingress, Service, NGINX Ingress Controller
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000032
Context
You must expose a web application using HTTPS routes.
Task
Create an Ingress resource named web in the prod namespace and configure it as follows:
. Route traffic for host web.k8s.local and all paths to the existing Service web
. Enable TLS termination using the existing Secret web-cert.
. Redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS .
You can test your Ingress configuration with the following command:
[candidate@cks000032]$ curl -L http://web.k8s.local
Task
Create a NetworkPolicy named pod-access to restrict access to Pod users-service running in namespace dev-team.
Only allow the following Pods to connect to Pod users-service:
 Pods in the namespace qa
Pods in the namespace qa
 Pods with label environment: testing, in any namespace
Pods with label environment: testing, in any namespace


Context
For testing purposes, the kubeadm provisioned cluster 's API server
was configured to allow unauthenticated and unauthorized access.
Task
First, secure the cluster 's API server configuring it as follows:
. Forbid anonymous authentication
. Use authorization mode Node,RBAC
. Use admission controller NodeRestriction
The cluster uses the Docker Engine as its container runtime . If needed, use the docker command to troubleshoot running containers.
kubectl is configured to use unauthenticated and unauthorized access. You do not have to change it, but be aware that kubectl will stop working once you have secured the cluster .
You can use the cluster 's original kubectl configuration file located at etc/kubernetes/admin.conf to access the secured cluster.
Next, to clean up, remove the ClusterRoleBinding
system:anonymous.
Cluster: qa-cluster
Master node: master Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context qa-cluster
Task:
Create a NetworkPolicy named restricted-policy to restrict access to Pod product running in namespace dev.
Only allow the following Pods to connect to Pod products-service:
1. Pods in the namespace qa
2. Pods with label environment: stage, in any namespace
Context
You must implement auditing for the kubeadm provisioned cluster.
Task
First, reconfigure the cluster 's API server, so that:
. the basic audit policy located at
/etc/kubernetes/logpolicy/audit-policy.yaml is used,
. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes/audit-logs.txt,
. and a maximum of 2 logs are retained for 10 days.
The cluster uses the Docker Engine as its container runtime . If needed, use the docker command to troubleshoot running containers.
The basic policy only specifies what not to log.
Next, edit and extend the basic policy to log:
. namespaces interactions at RequestResponse level
. the request body of deployments interactions in the namespace webapps
. ConfigMap and Secret interactions in all namespaces at the Metadata level
. all other requests at the Metadata level
Make sure the API server uses the extended policy.
Failure to do so may result in a reduced score.

