Oracle Oracle Inventory Cloud 2024 Implementation Professional 1z0-1073-24 Exam Dumps: Updated Questions & Answers (February 2026)
Goods need to be moved from Org A to Org B. The person at the warehouse in Org B must receive and move the shipment physically, and perform a quality check.Which is the appropriate transfer type and receipt routing required?
Your customer wants to reserve material for a future project. There is no existing demand document for this purpose.How can you create this reservation?
In your shipment integration between inventory cloud and the 3PL system, some shipment confirmation messages have errored.
How do you manage these pending transactions?
The interorganization parameter is not set up completely.Shipment numbers are not generated for transfers using direct organization transfer.Your customer has decided to implement dual UOM tracking for an inventory organization.
Which two statements are FALSE about dual UOM tracking?
Your supplier has reduced the supply quantity from 100 to 80 for a supply order with a requested quantity of 100. Supply Chain Orchestration is unable to find an alternative source of supply to meet this demand.
What will this supply line be grouped under?
Against a Purchase Order quantity of 100, your receiving agent has received 50 items in the receiving type subinventory. Later in the day, 25 items have been put away to inventory. What is the item availability in the Manage Item Quantity UI?
Steve, your warehouse manager, created a lot for an item by mistake. He is unable to disable this lot from the Manage Lots task.What could be the reason?
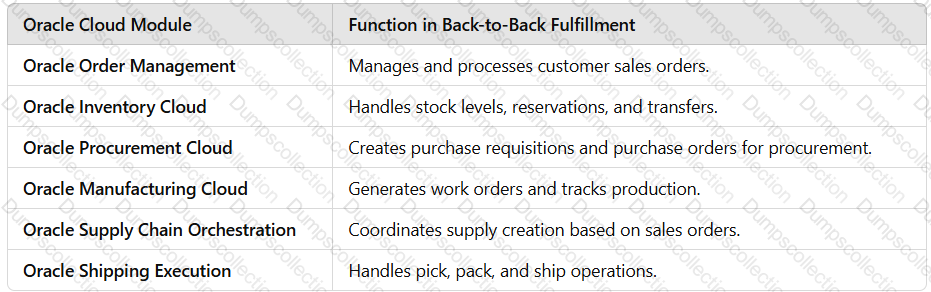
Back to Back fulfillment
Overview of Back-to-Back Fulfillment
The back-to-back fulfillment process is one in which specific sales order demand triggers supply creation, and a link is established between the sales order and the supply.
Note: Back-to-back flow is currently supported only for discrete manufacturing.
The following figure provides a high-level flow diagram showing the back-to-back supply creation and fulfillment process flow.
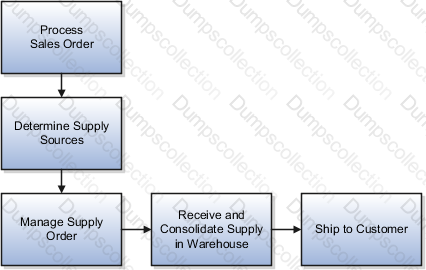
Back-to-back fulfillment is where supply is procured and then received at a warehouse only after an order is placed.
The supply is reserved against a sales order until shipping.
This process provides support to create and link supply after a sales order is entered and scheduled, allowing you to reduce your inventory while maintaining the ability to respond to customer demands.
You create supply for a back-to-back order using one or more of the following back-to-back flows:
•Buy: Procurement from an external supplier.
•Make: Production in an internal manufacturing facility (includes in-house manufacturing and contract manufacturing).
•Transfer: Transfer from another warehouse.
•On hand: Reservation of on-hand supply in the fulfillment organization.
Note: For information about back-to-back flows for contract manufacturing, see the Implementing Contract Manufacturing chapter in this guide.
After the supply is received into the fulfillment warehouse, the back-to-back order is ready for shipment to the customer.
Set Up Back-to-Back Transfer Flow
The topic explains what you need to do for setting up back-to-back transfer flow.
In the Oracle Product Information Management, ensure that the Item is Back-to-Back enabled.
In Oracle Global Order Promising:
1.Set up a global sourcing rule with Type as Transfer from. Set the organization as the organization requesting the transfer (example, Warehouse 1).
2.Set up a local sourcing rule for the organization (in this example, Warehouse 1) Type as Transfer from, from the organization that has the stock from which the transfer will take place (example, Warehouse 2).
3.Set up an ATP rule with the Promising Mode as Supply chain availability search.
4.Ensure that the Supply chain availability search attributes are enabled according to your requirements. For example, you might want the application to search components and resources to include on-hand or in-transit Supply Types or fulfillment lines Demand Types.
5.Set the ATP Rule Assignment as required.
6.Set the sourcing assignments for the sourcing rules that you defined in steps 1 and 2.
7.Ensure that the assignment level used for the global sourcing rule doesn't include any Organization.
8.Refresh and restart the Order Promising Server for ATP Rules and Sourcing.
With this setup:
•The global rule is used to source the item from Warehouse 1 if there is stock available to reserve.
•If there's no stock on hand, Global Order Promising uses the local rule to transfer the item from Warehouse 2 to Warehouse 1.
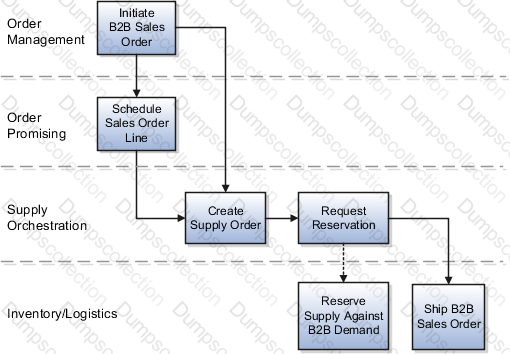
Back-to-Back Supply Creation On-Hand Flow
The back-to-back on-hand available (ATP) flow is the simplest in terms of the number of steps that constitute the flow. This flow occurs where on hand supply is available in the fulfillment warehouse for the ordered back-to-back item at the time of order promising. Because on-hand goods already exist in the form of on hand, Oracle Supply Chain Orchestration directly sends a request to reserve the on hand quantity against the back-to-back sales order. You can ship the sales order immediately after the reservation is created.
The following figure shows the back-to-back supply creation on-hand flow.

 A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.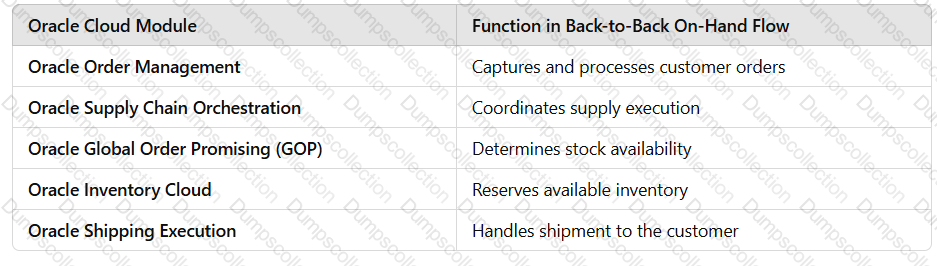 A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.