Salesforce Salesforce Certified MuleSoft Platform Integration Architect (Mule-Arch-202) MuleSoft-Integration-Architect-I Exam Dumps: Updated Questions & Answers (March 2026)
Mule application is deployed to Customer Hosted Runtime. Asynchronous logging was implemented to improved throughput of the system. But it was observed over the period of time that few of the important exception log messages which were used to rollback transactions are not working as expected causing huge loss to the Organization. Organization wants to avoid these losses. Application also has constraints due to which they cant compromise on throughput much. What is the possible option in this case?
Which Exchange asset type represents configuration modules that extend the functionality of an API and enforce capabilities such as security?
The implementation of a Process API must change. What is a valid approach that minimizes the impact of this change on API clients?
Mule application A receives a request Anypoint MQ message REQU with a payload containing a variable-length list of request objects. Application A uses the For Each scope to split the list into individual objects and sends each object as a message to an Anypoint MQ queue.
Service S listens on that queue, processes each message independently of all other messages, and sends a response message to a response queue.
Application A listens on that response queue and must in turn create and publish a response Anypoint MQ message RESP with a payload containing the list of responses sent by service S in the same order as the request objects originally sent in REQU.
Assume successful response messages are returned by service S for all request messages.
What is required so that application A can ensure that the length and order of the list of objects in RESP and REQU match, while at the same time maximizing message throughput?
An organization's IT team follows an API-led connectivity approach and must use Anypoint Platform to implement a System AP\ that securely accesses customer data. The organization uses Salesforce as the system of record for all customer data, and its most important objective is to reduce the overall development time to release the System API.
The team's integration architect has identified four different approaches to access the customer data from within the implementation of the System API by using different Anypoint Connectors that all meet the technical requirements of the project.
A project team is working on an API implementation using the RAML definition as a starting point. The team has updated the definition to include new operations and has published a new version to exchange. Meanwhile another team is working on a mule application consuming the same API implementation.
During the development what has to be performed by the mule application team to take advantage of the newly added operations?
Refer to the exhibit.
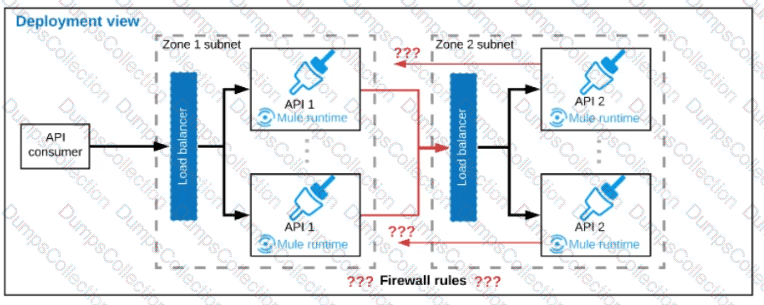
A business process involves two APIs that interact with each other asynchronously over HTTP. Each API is implemented as a Mule application. API 1 receives the initial HTTP request and invokes API 2 (in a fire and forget fashion) while API 2, upon completion of the processing, calls back into API l to notify about completion of the asynchronous process.
Each API Is deployed to multiple redundant Mule runtimes and a separate load balancer, and is deployed to a separate network zone.
In the network architecture, how must the firewall rules be configured to enable the above Interaction between API 1 and API 2?
A Mule application contains a Batch Job scope with several Batch Step scopes. The Batch Job scope is configured with a batch block size of 25.
A payload with 4,000 records is received by the Batch Job scope.
When there are no errors, how does the Batch Job scope process records within and between the Batch Step scopes?
A stock broking company makes use of CloudHub VPC to deploy Mule applications. Mule application needs to connect to a database application in the customers on-premises corporate data center and also to a Kafka cluster running in AWS VPC.
How is access enabled for the API to connect to the database application and Kafka cluster securely?
A Mule application is synchronizing customer data between two different database systems.
What is the main benefit of using eXtended Architecture (XA) transactions over local transactions to synchronize these two different database systems?

